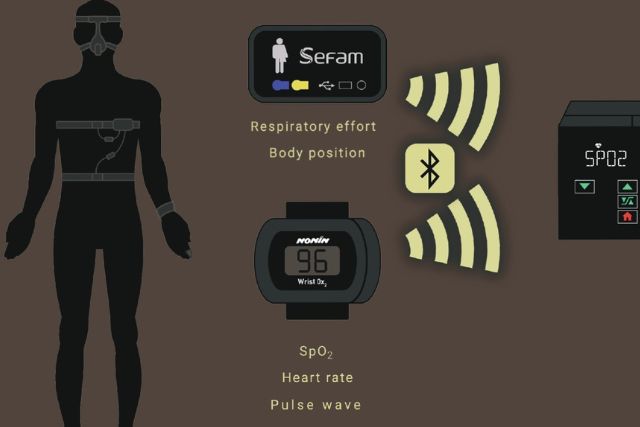
A variety of cutting-edge technological advancements are expected to influence the future of intensive care. These innovations have the potential to further improve patient care, clinical outcomes, and healthcare delivery efficiency.
Here are some of the latest technological advancements that are likely to play a pivotal role in the future of critical care:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning:
AI algorithms will develop more and become more complex in their analysis of patient data. They will support treatment plan optimization, patient outcome prediction, and early detection of deteriorating diseases. AI-driven decision support tools will help medical professionals make better decisions.
Telemedicine and Remote Monitoring:
Critical care will incorporate telemedicine more and more. Tele-ICUs and remote monitoring devices can be used to provide care for patients who live in remote locations or who need long-term monitoring. Access to specialized critical care services will thus be improved.
Wearable Devices:
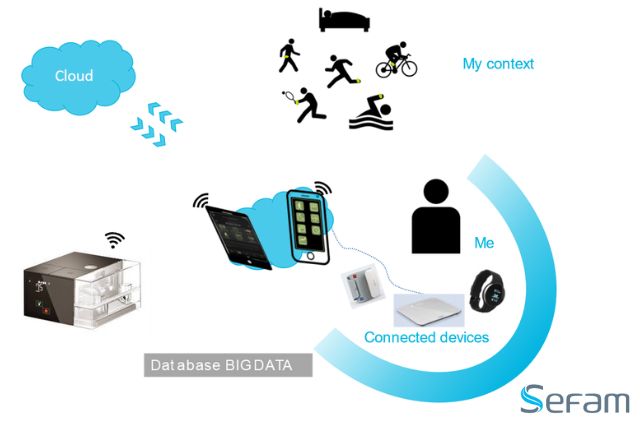
Wearable medical technology will spread more widely, enabling patients to continuously check their vital signs and health state. These gadgets will give healthcare professionals and patients access to real-time data, allowing for earlier chronic condition management and early intervention.
Robotics and Automation:
In order to help with duties like medicine administration, patient transportation, and routine monitoring, robots and automated technologies will play a bigger part in patient care in the future. They can lessen the effort for medical workers and lower the possibility of human error.
Advanced Imaging:
Medical imaging advancements like portable, high-resolution CT scanners and MRI equipment will make it possible to diagnose and monitor patients in critical care more quickly and accurately. By doing so, problems will be identified earlier and treatment choices will be more informed.
Genomic Medicine:
Critical care will incorporate genomic sequencing more and more. Knowing a patient’s genetic predispositions can be used to customize medications and treatment strategies, increasing their efficacy and lowering side effects.
Precision Medicine:
Precision medicine developments will make it possible to customize therapies depending on each patient’s particular traits. This strategy will produce medications that are more focused, effective, and have fewer adverse effects.
Biotechnology and Pharmaceuticals:
New choices for critical care patients will be made available by the development of new pharmaceuticals and biotechnological therapies, such as gene therapies and regenerative medicine, which may facilitate tissue regeneration and recovery.
Data Integration and Interoperability:
Health care systems will be able to share patient data more easily, minimizing the need for repeated testing and ensuring that healthcare practitioners have access to complete patient information as a result of improved data integration and interoperability.
Patient Engagement Tools:
Platforms for patient involvement will increase in personalization and interactivity. Through user-friendly interfaces, patients will have access to their health information, treatment plans, and educational resources, increasing their involvement in their care.
Ethical and Legal Considerations:
The need to address ethical and legal concerns relating to data privacy, patient consent, and liability in the use of new critical care technologies will grow as technology develops.
Environmental Considerations:
Healthcare facilities will put more emphasis on environmental impact and sustainability, integrating eco-friendly practices and technologies into critical care units.
In conclusion, a convergence of cutting-edge technologies that improve clinical decision-making, enhance patient care, and encourage patient engagement is poised to revolutionize the future of critical care. These developments promise to deliver crucial care that is more accurate, tailored, and effective, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and the healthcare experience as a whole. To ensure these technologies’ responsible and advantageous deployment in critical care settings, it is crucial to negotiate the difficulties and ethical issues related to them.