Head and neck cancer is a term used to define cancer that develops in the mouth, throat, nose, salivary glands, oral cancers or other areas of the head and neck. 85% of head and neck cancers are linked to tobacco use and 75% are associated with a combination of tobacco and alcohol use.
Here are the few myths relating to head and neck cancers.
I am a smoker/tobacco chewer. I won’t get cancer as I brush my mouth daily
The carcinogens from tobacco are directly absorbed from the inner lining of the mouth (mucosa). They are not removed by brushing or rinsing of mouth.
Biopsy will result in cancer
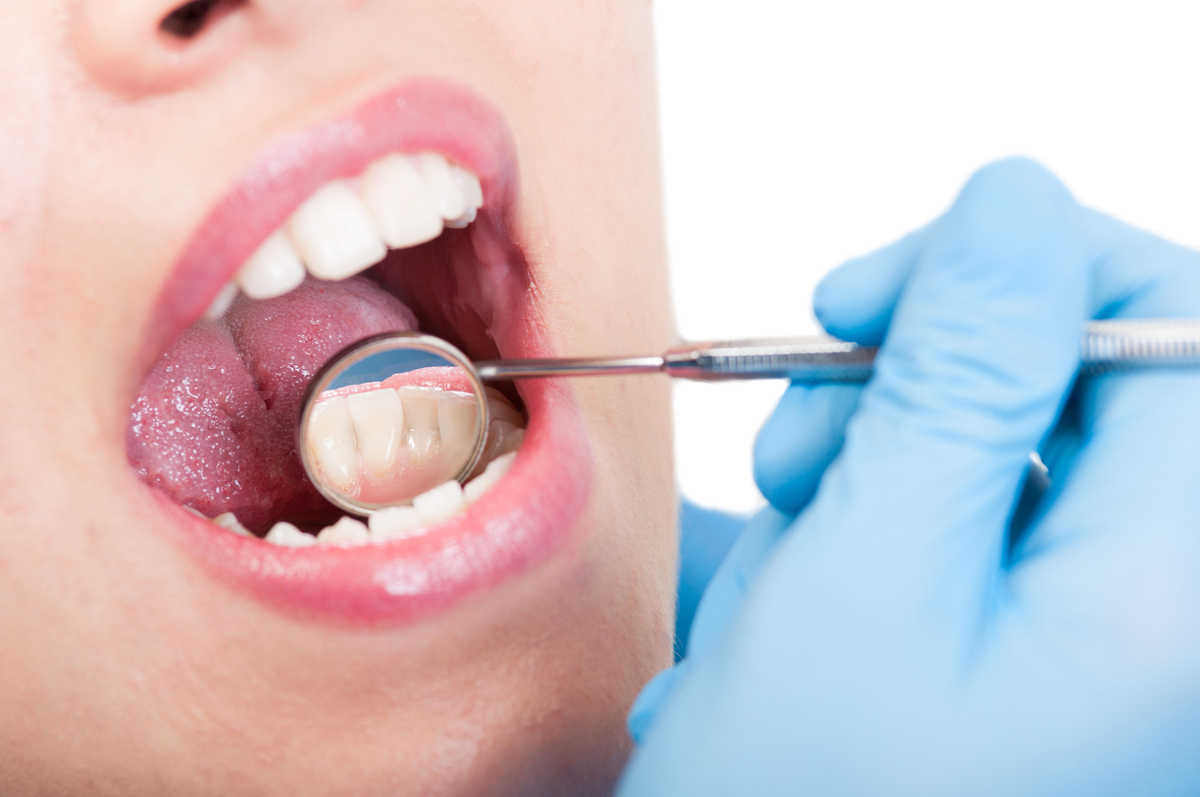
Biopsy is the only reliable way in which oral cancer can be confirmed. Biopsy is done if cancer is suspected. Biopsy itself does not cause cancer. Early detection can lead to early and better treatment.
Oral cancer can be detected by blood test
The only reliable way to confirm oral cancer is to take a biopsy. Currently, there are no blood tests available to confirm or refute oral cancer. Early detection can lead to early and better cure.
I have oral cancer, and “cancer has no answer”, isn’t it?
Oral cancer is one of the most common cancer in India. Most patients who have oral cancer, present late and thus the treatment becomes difficult. However, like most other cancers, oral cancers can definitely be treated with good success, and the results can definitely improve if the disease can be detected early.
Surgery is very painful. Surgeries are very risky.
Contrary to popular belief, surgeries are not painful. Modern anaesthesia with good safety measures make surgery acceptable. Even long duration surgeries can now be performed safely.
I will never be able to eat after oral cancer surgery.
Although oral cancer surgeries are morbid, most surgical removals (excisions) can be reconstructed safely. This allows for early rehabilitation for most patients and most patients are able to eat normal to near-normal food post-surgery.
Radiation is harmful for body
Modern radiation machines are linear accelerator machines which emit radiation only when switched on. Modern radiation techniques can effectively contour radiation areas to spare vital structures like spine, brain, eyes, salivary glands and blood vessels thereby reducing toxicity without compromising on efficacy.
Cancer is contagious, right?
No, oral cancer is not contagious. Patients can safely stay and enjoy the company of friends and family and even share food and stay together. They can continue with their usual physical, sexual and professional life as before. Currently, there’s no research which suggests any inheritance pattern of this group of cancer.
Oral cancer is disease of males.
Although oral cancers are more prevalent in males, it is probably related to the pattern of use of tobacco or supari. Oral cancer is among the top 5 cancers in females in India and there is a rising trend.
Oral cancers are painful. My oral ulcer is painless, so it is not cancer.
Most oral cancers present as painless non-healing ulcers in the mouth. The pain in oral cancers is usually due to involvement of nerve, bone or deep tissue penetration and is a sinister sign of advanced disease. Do not wait for pain – if you have an oral ulcer which has persisted for more than 15 days, seek immediate opinion of a doctor specialised in oral cancer management.
Tobacco causes cancer but supari is safe
Supari contains arecoline and other harmful chemicals which act as carcinogens and are responsible for causing cancer.
There’s a safe limit for cigarettes.
Even smoking one cigarette a day is known to increase the risk of oral cancer significantly. Smoking and other forms of tobacco usage carries a significant risk of oral cancer.
Drinking alcohol is safe.
Alcohol gets converted to aldehydes in the oral cavity by commensal bacteria and is a known carcinogen. Alcohol has a synergistic effect with tobacco to increase the risk of developing oral cancer.
e-cigarettes and Hookahs don’t cause cancer.
The carcinogens present in e-cigarettes and Hookahs are the same as in normal smoked cigarettes and are equally harmful.
Myths about Oral Cancer