The outbreak of Covid19 in December 2019 has once again brought zoonotic infections into focus. As per WHO estimates, 61 percent of all human diseases are zoonotic in origin.
Zoonotic (or Zoonosis) are infections or diseases that can be transmitted between animals and humans – like dengue, malaria, chikungunya, rabies, salmonella infection, E coli infection, Lyme disease, psittacosis, Ebola, anthrax, bird flu (avian), swine flu, zika fever, etc. There are over 200 diseases that are transmittable from animals to humans. Zoonoses may be dangerous and even cause death if not diagnosed and treated on time.
In recent years, epidemiological safety has been threatened by emerging zoonotic diseases. Studies place 75% of emerging pathogens are zoonotic.
There is still insufficient data available to categorize Covid19 as Zoonotic. Furthermore, while the initial hype attributed the spread of Covid19 to the bats and sea-foods market, no animal reservoirs for the Covid19 infections were found. Nonetheless, we must understand the zoonotic category of diseases so that we may prevent and control them.
Metagenomics is an alternative to getting genome sequences of different microorganisms, which comprise a microbial community.
Understanding the Causes & Transmission
Humans worldwide have intimate contact with animals – as pets, on farms, in the wild, and in our habitat. Animals are essential in our daily lives.
They inhabit our houses and are an integral part of the agricultural practices around the world.
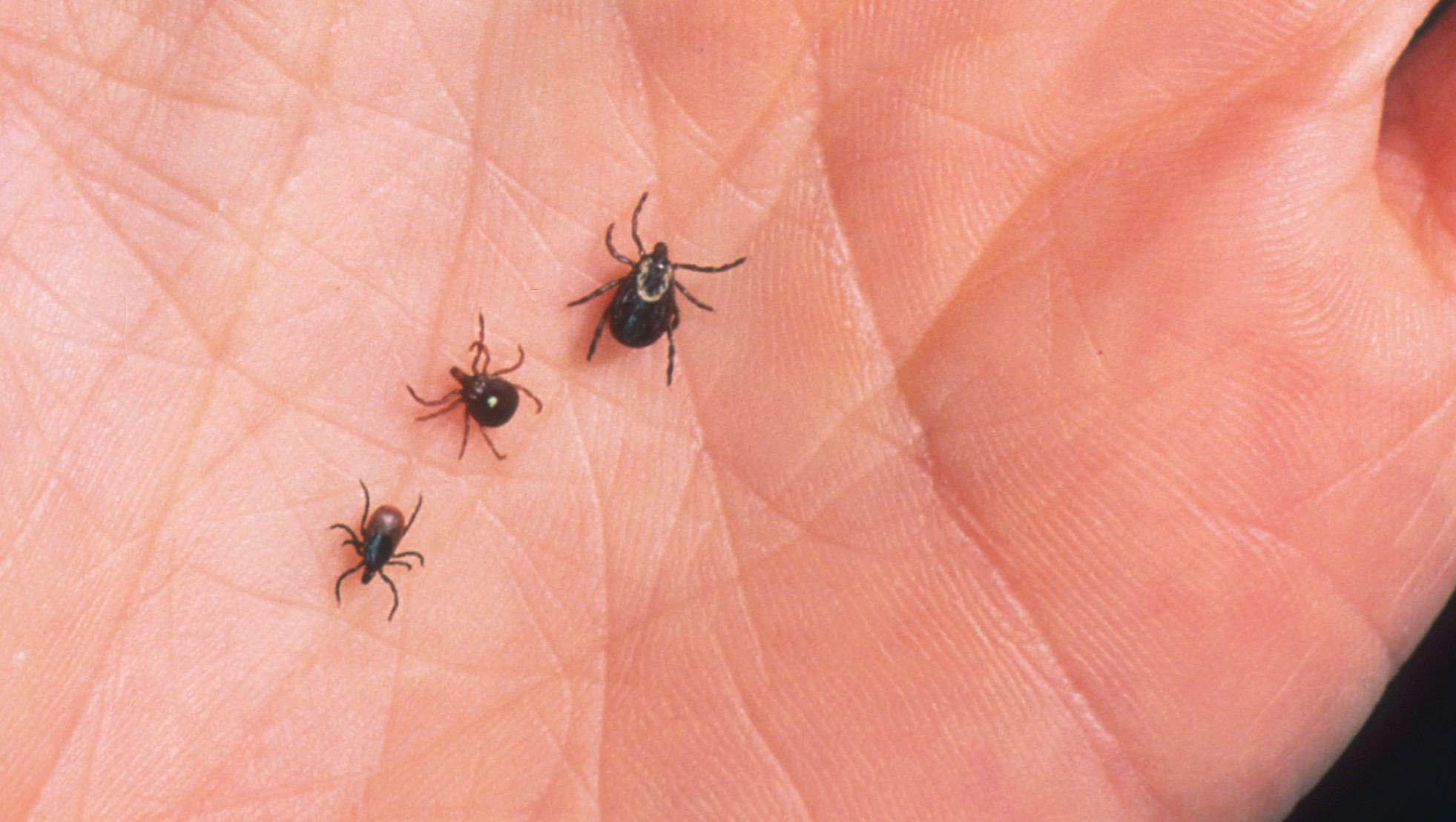
The saliva, blood, urine, or faeces of animals, which are infected, transmit zoonotic agents. Zoonotic infections can be contracted via animal bites, arthropod vectors, especially ticks and mosquitoes, and direct contact with animals. Diseases also can be contracted indirectly by ingestion of contaminated food or water or contact with contaminated hides, wool, or fur. Several animals are only carriers of different pathogens for humans. Mosquito is the most prominent vector and primarily the causal agent of dengue and malaria. The zoonotic disease may also be contracted or spread through contaminated food consumption. It is a commonplace to consume unpasteurized milk, undercooked meat or fish, and unwashed fruits and vegetables, which can be contaminated with urine and faeces from infected animals.
Who’s Most at Risk
Apart from infected food consumption, persons at risk of zoonotic infections include people who enjoy outdoor leisure activities such as hiking, camping, hunting, and fishing. Occupational groups at risk have animal control officers, hunters, abattoir workers, farmers, fisherpersons, persons working with hides or wool, and laboratory workers working with zoonotic pathogens.
The risk of infection can be reduced by the appropriate use of personal protective equipment, immunizations, and measures to avoid insect bites.
Diagnosis Techniques
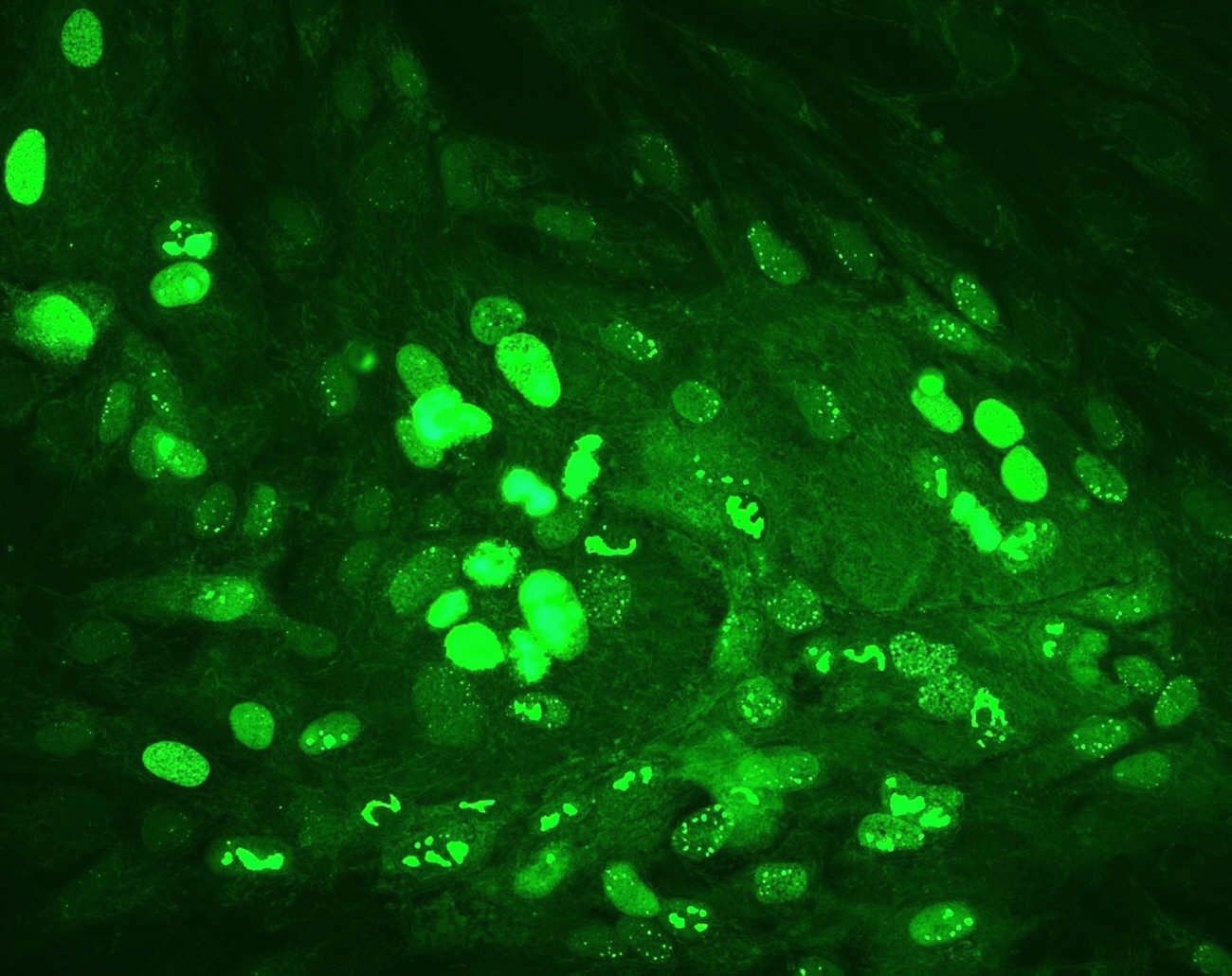
Various methodologies have been developed to diagnose Zoonosis, including culture-dependent and immunological-based methods, which allow the identification of a vast range of pathogens. Rapid and Elisa tests are the front-runners in diagnosing zoonotic diseases because of their ease of use and the ability to conduct these tests in any setting / point-of-care location. Molecular tests have been designed and developed to identify a single pathogen or mixtures. Metagenomics is an alternative to getting genome sequences of different microorganisms, which comprise a microbial community. Metagenomics has been used to depict microbiomes and viromes, which are not cultivable under laboratory conditions. This methodology could be a powerful tool in diagnosing zoonotic diseases because it allows the identification of genus and species and the detection of some proteins in specific conditions on specific tissues through structural and functional metagenomics.
Authored By:
Jatin Mahajan
Managing Director
J Mitra & Co.
India’s leading IVD company