Histopathology equipment is used in pathology to examine tissue samples in order to diagnose diseases, investigate cellular architecture, and conduct research.
This comprehensive overview provides an insight into the essential equipment used in histopathology laboratories:
Microscopes:
Light Microscopes:
Pathologists mostly utilize these to examine and interpret stained tissue slices. Light microscopes of high quality with a variety of objective lenses and magnification options are required.
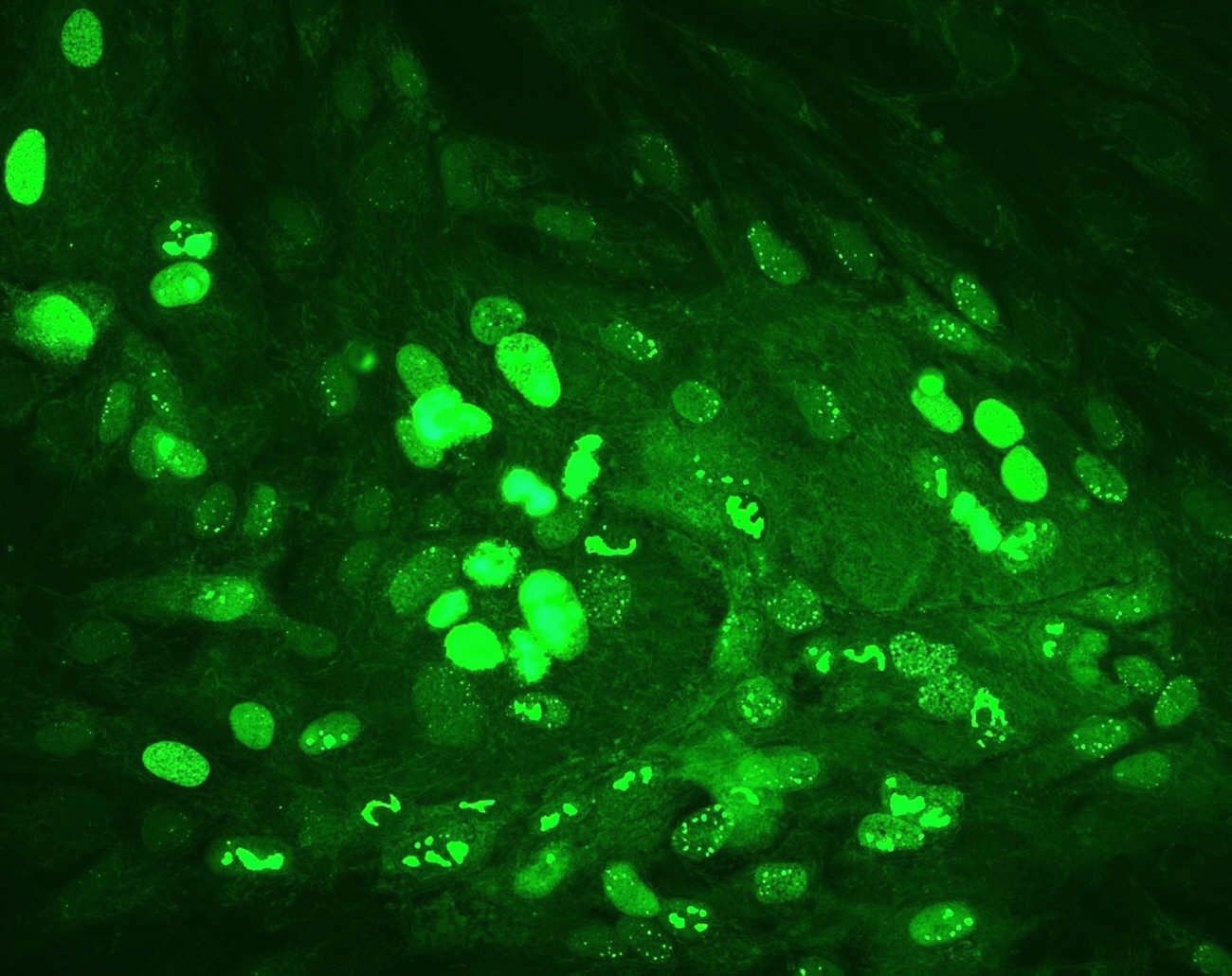
Fluorescence Microscopes:
These microscopes are outfitted with specialized filters and light sources that allow them to observe fluorescently labeled tissue components or biomolecules.
Cryostats:
Cryostats are used to cut thin, frozen slices of tissue. They keep tissue blocks cold and allow for precision sectioning of frozen specimens for quick analysis.
Microtomes:
Microtomes are used to make thin sections of tissue blocks that have been paraffin-embedded. These sections are then stained and examining on slides.
Tissue Processors:
Tissue processors automate the dehydration, cleaning, and paraffin embedding processes. They boost efficiency by streamlining the tissue preparation procedure.
Embedding Centers:
Embedding centers are used to embed tissue samples in paraffin wax blocks, allowing them to be sectioned with a microtome.
Slide Stainers:
Slide Stainers automate the staining of tissue slices with common histological stains like hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), as well as specialty stains for specific structures or biomolecules.
Automated Immunostainers:
These immunohistochemistry (IHC) machines can automate the staining of tissue slices with specific antibodies to detect certain proteins or antigens.
Tissue Floatation Baths:
Floatation baths are used to warm water to a controlled temperature so that tissue slices can be flattened and stretched on the water’s surface before being transferred to slides.
Tissue Flotation Workstations:
For efficient tissue section preparation, these workstations contain a flotation bath, slide warmer, and drying oven.
Tissue Slide Warmers:
Slide warmers keep tissue sections on glass slides at the ideal temperature for adhesion and drying.
Ovens and Incubators:
Incubators provide controlled temperature and humidity conditions for tissue culture, whilst drying ovens are used to dry stained slides after staining.
Coverslippers:
Coverslippers attach glass coverslips to tissue sections on slides to protect and preserve them.
Cytocentrifuges:
Cytocentrifuges are used to prepare cytology smears for microscopic examination by concentrating cells onto slides.
Autostainers:
Autostainers automate the staining of cytology and hematological slides, increasing consistency while decreasing manual work.
Molecular Pathology Equipment:
For molecular analysis of tissue samples, instruments such as PCR machines, DNA sequencers, and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) systems are utilized.
Image Analysis Systems:
Digital imaging systems, such as whole-slide scanners, enable the collection and storing of high-resolution images of complete tissue sections for remote viewing and analysis.
Safety Equipment:
Safety cabinets, fume hoods, and personal protective equipment (PPE) are crucial for guaranteeing laboratory personnel’s safety when handling dangerous chemicals or infectious materials.
Quality Control Instruments:
Quality control equipment, such as microtome blade sharpeners, is used to preserve the precision and quality of tissue sections.
Freezers and Refrigerators:
Freezers and refrigerators are used to keep tissue samples, reagents, and antibodies at the proper temperatures.
Laboratory Information Systems (LIS):
LIS software aids in the effective management and tracking of patient data, specimen information, and laboratory results.
The integration of these important equipment and devices in a histopathology laboratory is critical for accurate disease detection and the advancement of medical research. The equipment chosen should be appropriate for the laboratory’s specific demands and the types of tests undertaken, whether they entail standard clinical pathology, research, or specialist testing. Regular maintenance and calibration are also necessary to assure the accuracy and dependability of the results.